Author: Ulink Media
Everyone should be familiar with 5G, which is the evolution of 4G and our latest mobile communication technology.
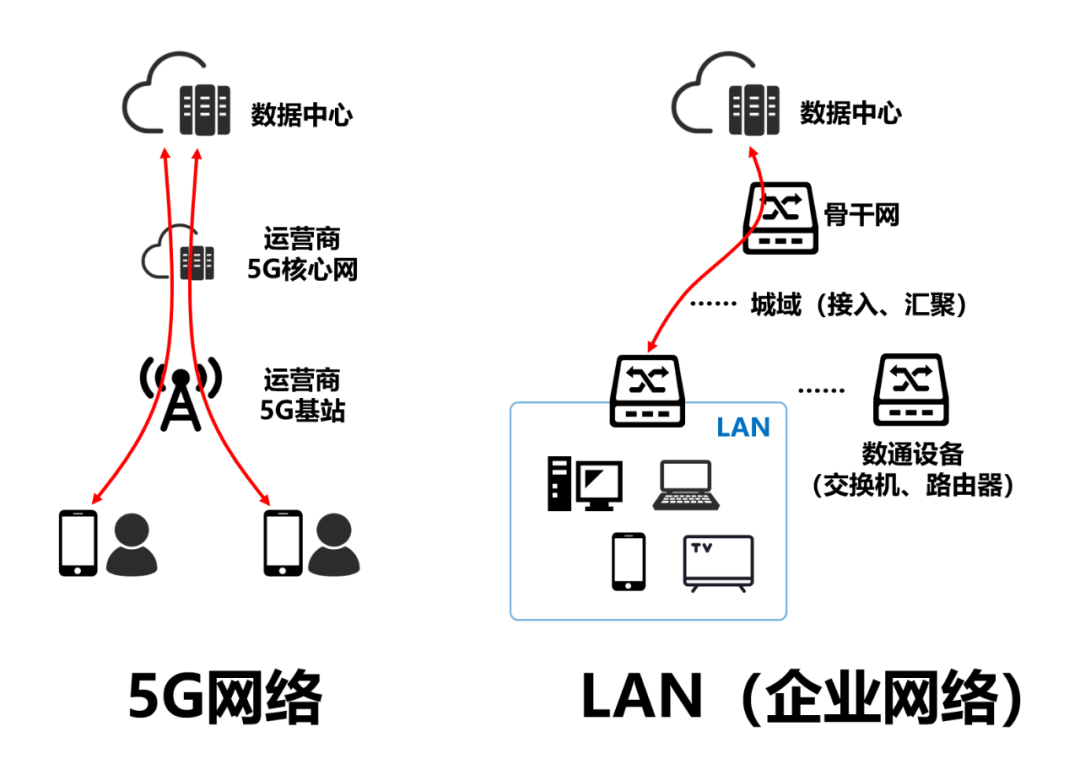
For LAN, you should be more familiar with it. Its full name is local area network, or LAN. Our home network, as well as the network in the corporate office, is basically LAN. With Wireless Wi-Fi, it is a Wireless LAN (WLAN).
So why am I saying 5G LAN is interesting?
5G is a broad cellular network, while LAN is a small area data network. The two technologies seem unrelated.
In other words, 5G and LAN are two words that everyone knows separately. But together, it’s a little confusing. Isn’t it?
5G LAN, What Exactly It Is?
In fact, 5G LAN, to put it simply, is to use 5G technology to “group” and “build” terminals to form a LAN network.
Everyone has a 5G phone. When you’re using 5G phones, have you noticed that your phone can’t search for your friends even when they’re in close proximity (even face to face)? You can communicate with each other because the data flows all the way around to the servers of your carrier or Internet service provider.
For base stations, all mobile terminals are “isolated” from each other. This is based on security considerations, the phones use their own channels, do not interfere with each other.
A LAN, on the other hand, connects terminals (mobile phones, computers, etc.) in an area together to form a “group”. This not only facilitates the data transmission between each other, but also saves the extranet exit.
In a LAN, terminals can locate each other based on their MAC addresses and find each other (Layer 2 communication). To access the external network, set up a router, through the IP location, can also achieve routing in and out (Layer 3 communication).
As we all know, “4G will change our lives, and 5G will change our society”. As the most mainstream mobile communication technology at present, 5G shoulders the mission of “the Internet of everything and the digital transformation of hundreds of lines and thousands of industries”, which needs to help users in vertical industries get connected.
Therefore, 5G cannot only connect every terminal to the cloud, but also realize “nearby connection” between terminals.
Therefore, in the 3GPP R16 standard, 5G LAN introduced this new feature.
Principles and Characteristics of 5G LAN
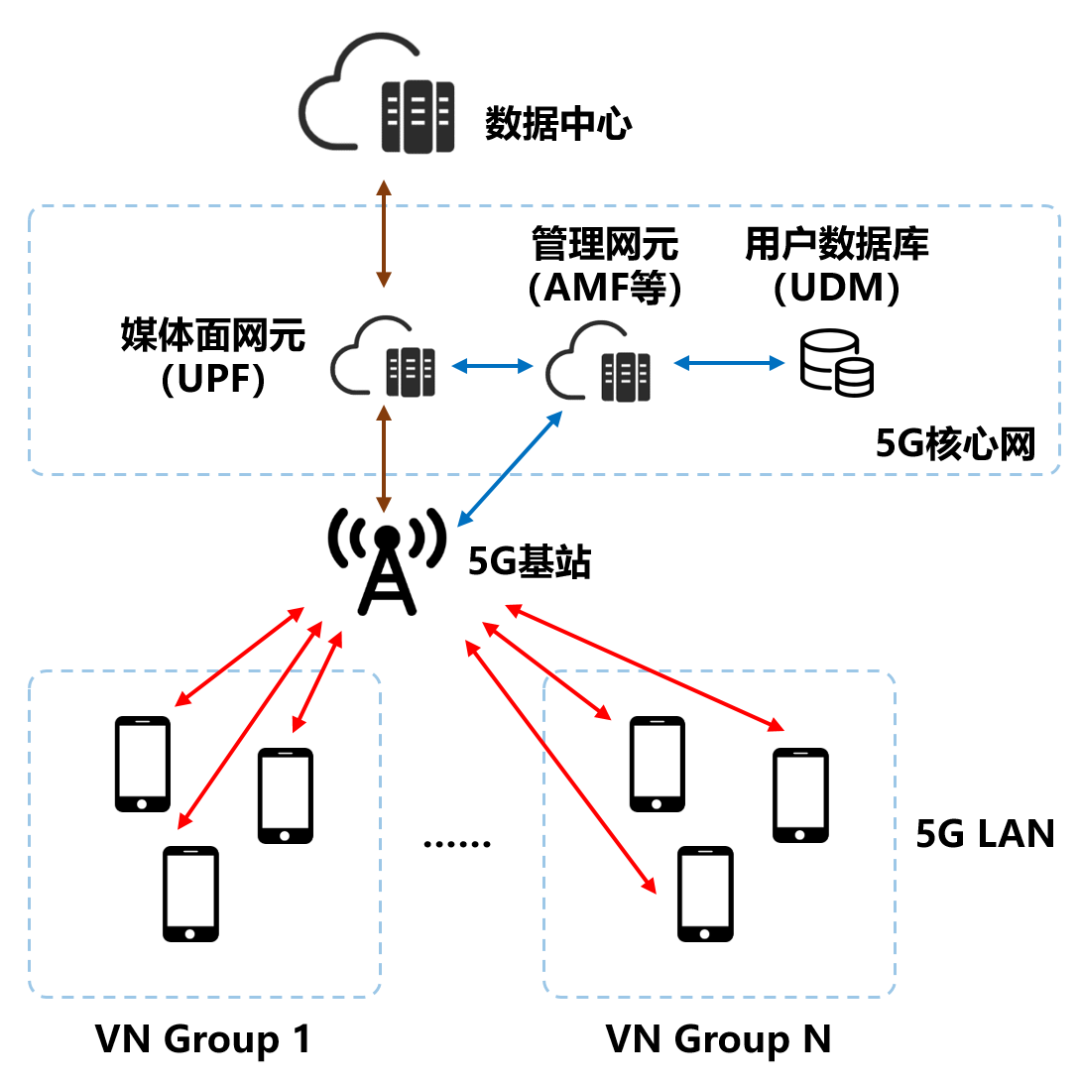
In a 5G Network, administrators can modify the data in the user database (UDM network elements), sign a service contract with a specified UE number, and then divide them into the same or different Virtual network groups (VN).
The user database provides terminal number VN group information and access policies to the management network elements (SMF, AMF, PCF, etc.) of the 5G core network (5GC). The management NE combines these information and policy rules into different Lans. This is a 5G LAN.
A 5G LAN supports Layer 2 communication (same network segment, direct access to each other) as well as Layer 3 communication (across network segments, with the help of routing). A 5G LAN supports unicast as well as multicast and broadcast. In short, the mutual access mode is very flexible, and the networking is very simple.
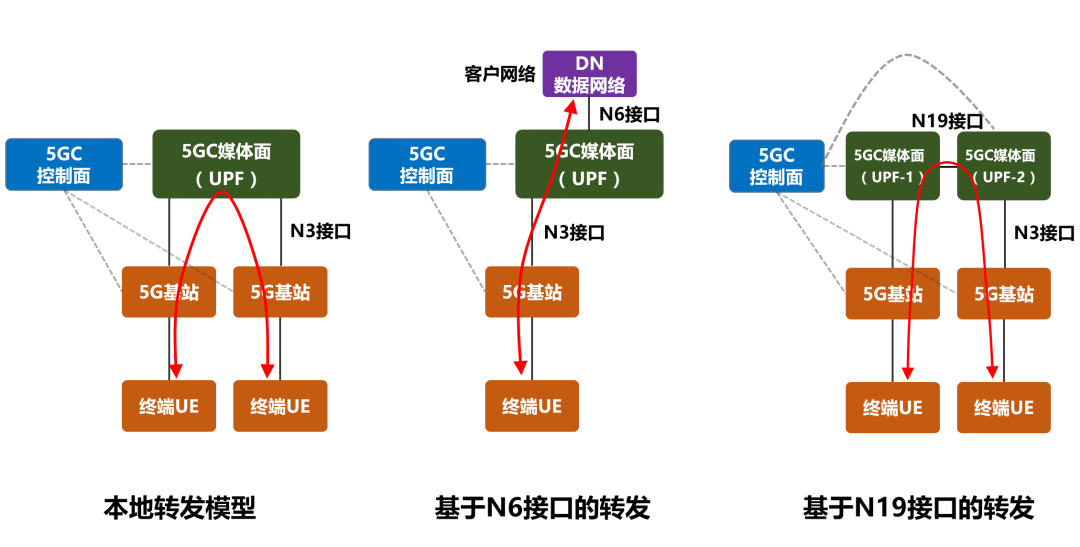
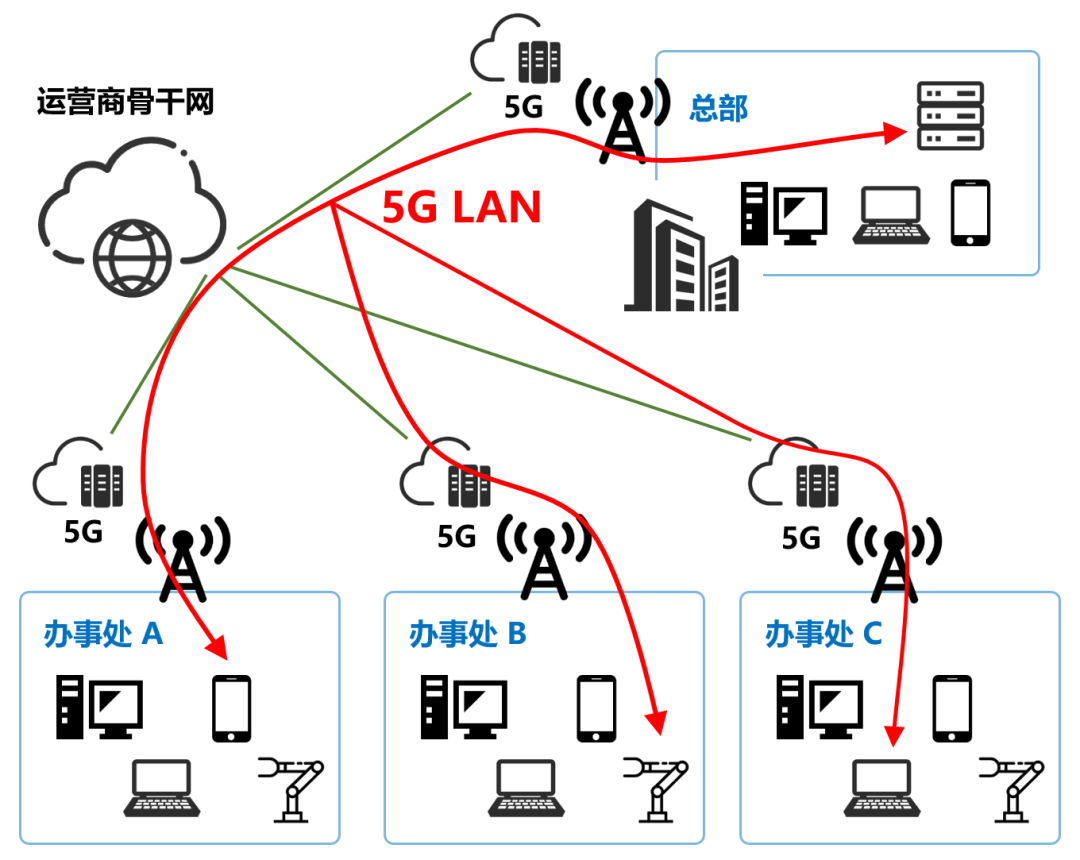
In terms of scope, a 5G LAN supports the communication between the same UPF (media side network element of the 5G core network) and different UPFs. This is tantamount to breaking the physical distance limit between terminals (even Beijing and Shanghai can communicate).
In particular, 5G LAN networks can connect to users’ existing data networks for plug and play and mutual access.
Application Scenarios And Advantages of 5G LAN
5G LAN enables the grouping and connection between specified 5G terminals, greatly facilitating the construction of a more mobile LAN network for enterprises. Many readers are sure to ask, isn’t mobility already possible with existing Wi-Fi technology? Why the need for a 5G LAN?
Don’t worry, let’s move on.
The local networking enabled by 5G LAN can help enterprises, schools, governments, and families better communicate with terminals in a region. It can be used in the office network, but its greater value lies in the transformation of the production environment of the park and the transformation of the basic network of production enterprises such as industrial manufacturing, port terminals and energy mines.
We are now promoting the industrial Internet. We believe that 5G can enable the digitalization of industrial scenes because 5G is an excellent wireless communication technology with large bandwidth and low delay, which can realize the wireless connection of various production factors in industrial scenes.
Take industrial manufacturing, for example. Previously, in order to better automation, to achieve equipment control, the use of “industrial bus” technology. There are many types of this technology, which can be described as “all over the place”.
Later, with the emergence of Ethernet and IP technology, the industry formed a consensus, together with the evolution of Ethernet, there is “industrial Ethernet”. Today, no matter who’s industrial interconnection protocol, basically is Ethernet-based.
Later, industrial companies found that wired connections limited mobility too much — there was always a “braid” at the back of the device that prevented free movement.
Moreover, the wired connection deployment mode is more troublesome, the construction period is long, the cost is high. If there is a problem with the equipment or cable, the replacement is also very slow. So, the industry began to think about introducing wireless communication technology.
As a result, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth and other technologies have entered the industrial field.
So, to return to the previous question, why 5G LAN when there is Wi-Fi?
Here’s the reason:
1. The performance of Wi-Fi networks (especially Wi-Fi 4 and Wi-Fi 5) is not as good as 5G.
In terms of transmission rate and delay, 5G can better meet the needs of industrial robots (manipulator control), intelligent quality inspection (high-speed image recognition), AGV (unmanned logistics vehicle) and other scenarios.
In terms of coverage, 5G has a larger coverage area than Wi-Fi and can better cover the campus. 5G’s ability to switch between cells is also stronger than Wi-Fi, which will bring users a better network experience.
2. Wi-Fi network maintenance costs are high.
To build a Wi-Fi network in a park, enterprises need to wire and buy their own equipment. Equipment is depreciated, damaged and replaced, but also maintained by special personnel. There are tons of Wi-Fi devices, and configuration is a hassle.
5G is different. It is built and maintained by operators and rented by enterprises (Wi-Fi versus 5G is a bit like building your own room versus cloud computing).
Taken together, 5G will be more cost-effective.
3. 5G LAN has more powerful functions.
The VN grouping of a 5G LAN was mentioned earlier. In addition to the isolation of communication, a more important function of grouping is to achieve the QoS (service level) differentiation of different networks.
For example, an enterprise has an office network, an IT system network, and an OT network.
OT stands for Operational Technology. It is a network that connects the industrial environment and equipment, such as lathes, robotic arms, sensors, instrumentation, AGVs, monitoring systems, MES, PLCS, etc.
Different networks have different performance requirements. Some require low latency, some require high bandwidth, and some have less requirements.
A 5G LAN can define different network performance based on different VN groups. Some enterprises, it is called “micro slice”.
4. 5G LAN is easier to manage and more secure.
As mentioned above, user signing data can be modified in 5G UDM nes of carriers to group users into VN groups. So, do we have to go to the carrier customer service every time we need to change the group information of a terminal (join, delete, change)?
Of course not.
In 5G networks, operators can open the modification permission to enterprise network administrators through the development of interfaces, enabling self-service modification.
Of course, enterprises can also set their own private network policies according to their own needs.
When establishing data connections, enterprises can set authorization and authentication mechanisms to strictly manage VN groups. This security is much stronger and more convenient than Wi-Fi.
A case study of a 5G LAN
Let’s take a look at the benefits of 5G LAN through a specific networking example.
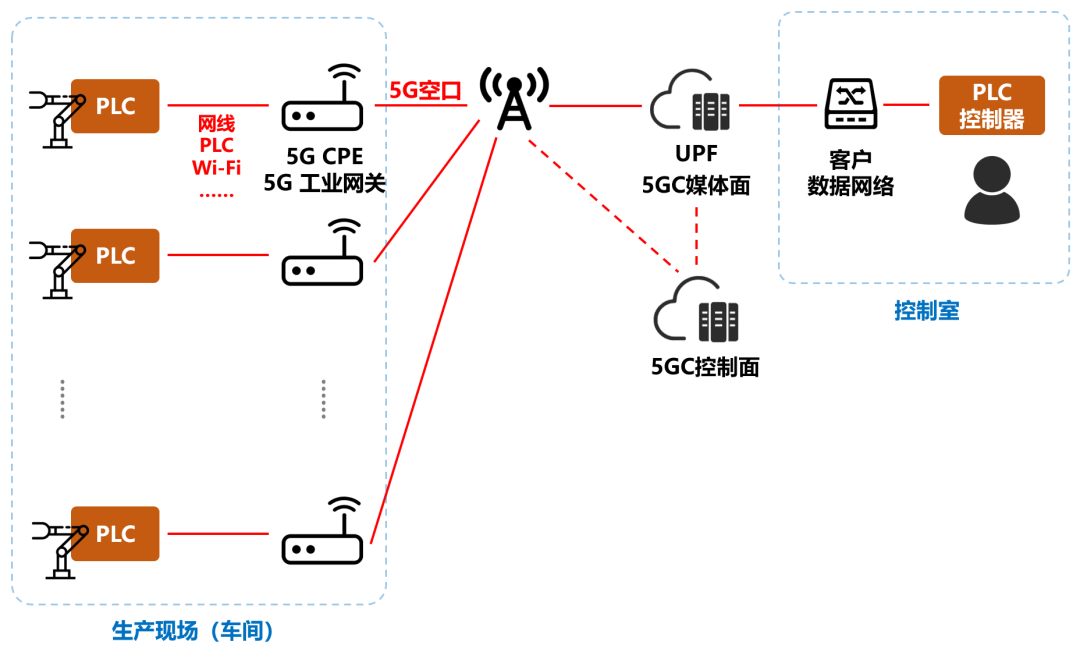
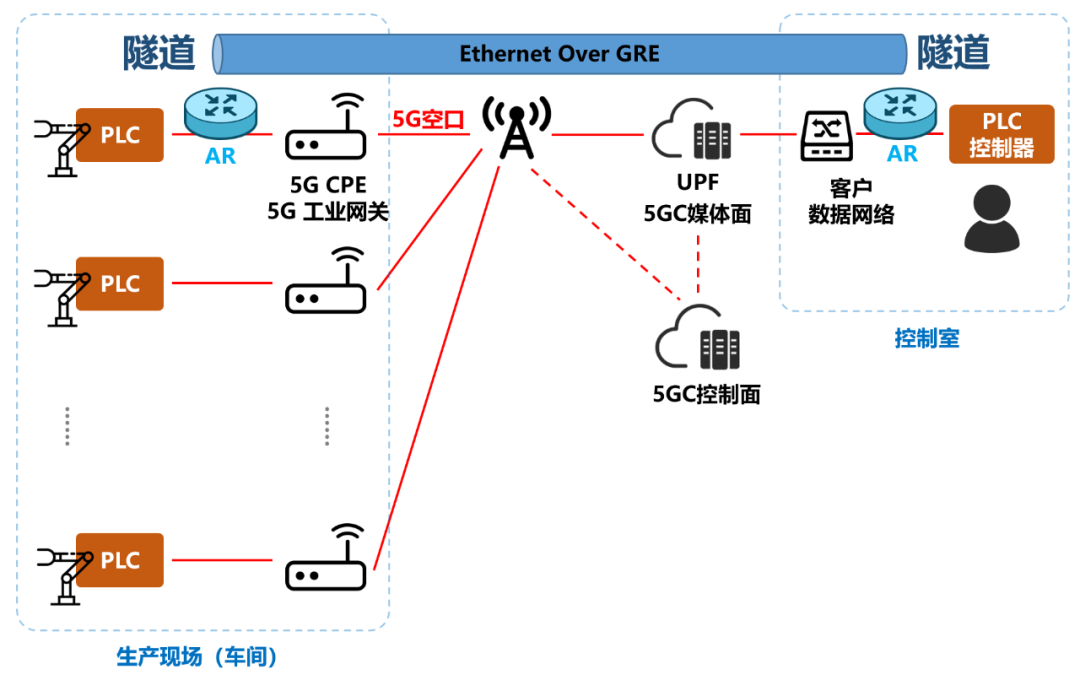
First of all, a manufacturing enterprise, has its own workshop, production line (or lathe), need to connect PLC and PLC control end through the network.
Each assembly line has a lot of equipment, also independent. It is ideal to install 5G modules on every device in the assembly line. However, it looks like it will be a bit expensive at this stage.
Then, the introduction of 5G industrial gateway, or 5G CPE, can improve the cost performance. Suitable for wired, connected to wired port (Ethernet port, or PLC port). Suitable for wireless, connected to 5G or Wi-Fi.
If 5G does not support 5G LAN (before R16), it is also possible to realize the connection between PLC and PLC controller. However, the entire 5G network is a Layer 3 protocol that relies on IP addressing, and the terminal address is also an IP address, which does not support Layer 2 data forwarding. In order to realize end-to-end communication, an AR (Access Router) must be added on both sides to establish a tunnel, encapsulate the industrial Layer 2 protocol in the tunnel, and bring it to the peer end.
This method not only increases the complexity, but also increases the cost (AR router purchase cost, AR router configuration manpower and time cost). If you think about a workshop with thousands of lines, the cost would be staggering.
After the introduction of 5G LAN, 5G network supports the direct transmission of Layer 2 protocol, so AR routers are no longer needed. At the same time, the 5G network can provide routes for terminals without IP addresses, and the UPF can recognize the MAC addresses of terminals. The entire network becomes a minimalist single-layer network, which can communicate with each other at layer 2.
The plug and play capability of 5G LAN can perfectly integrate itself with customers’ existing networks, reducing the impact on customers’ existing networks, and saving a lot of costs without strenuous renovation and upgrading.
From a macro perspective, 5G LAN is a collaboration between 5G and Ethernet technology. In the future, the development of TSN (time sensitive network) technology based on Ethernet technology can not be separated from the help of 5G LAN.
It is worth mentioning that 5G LAN, in addition to being conducive to the construction of the internal network of the park, can also be used as a supplement to the traditional dedicated line network of enterprises to connect branches in different places.
The module for the 5G LAN
As you can see, 5G LAN is an important innovative technology for 5G in vertical industries. It can build stronger 5G private network communications to help customers accelerate their digital transformation and upgrading.
In order to better deploy 5G LAN, in addition to network side upgrades, 5G module support is also needed.
In the process of 5G LAN technology commercial landing, Unigroup Zhangrui launched the industry’s first 5G R16 Ready baseband chip platform — V516.
Based on this platform, Quectel, the leading module manufacturer in China, has successfully developed a number of 5G modules supporting 5G LAN technology, and has been commercialized, including RG500U, RG200U, RM500U and other LGA, M.2, Mini PCIe package modules.
Post time: Dec-06-2022